Proff. Annachiara Cagnin, Diego Cecchin and colleagues published a paper about brain amyloid PET analysis


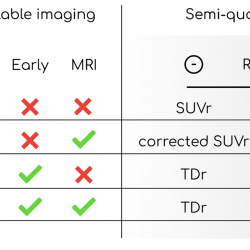
To date, there is no consensus on how to semi-quantitatively assess brain amyloid PET.
Researchers used data from 85 patients who underwent dual time-point PET/MRI acquisitions. The correlations with a gold standard (SI) were computed and the methods compared with the visual assessment.
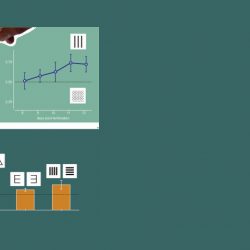
Each quantifier exhibited excellent agreement with visual assessment and strong correlation with SI (average AUC = 0.99, ρ = 0.91). Among the other methods, TDr came closest to the reference with less implementation complexity.
The ability of techniques integrating blood perfusion to depict age-related variations in amyloid load in amyloid-negative subjects demonstrates the goodness of the estimate.